|
Pandemic influenza A (H1N1) situation report of Japan, update 26
December 18, 2009
According to the National Epidemiological Surveillance for Infectious Diseases in Japan, the numbers of reported cases of the Influenza like Illness (ILI) have decreased in the 50th epidemiological week (December 7-13, 2009) (Figure 1). The number of cases reported per sentinel* in Japan was 27.39, which has decreased for two consecutive weeks. Based on this number, newly diagnosed ILI patients during this week are estimated to be approximately 1.32 million nationwide.
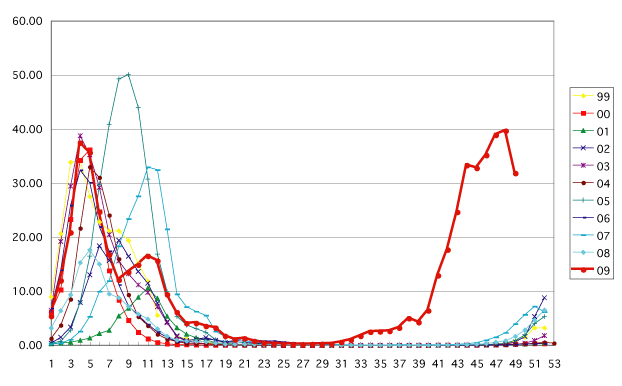
Figure 1. Weekly Influenza cases reported per sentinel
During the 50th epidemiological week (December 7-13, 2009), influenza activity
has decreased all except six prefectures. In comparison with the last week,
Oita Prefecture decreased 31% (from 54.69/sentinel to 37.83/sentinel) which
was the highest rate of reduction, followed by Kagawa Prefecture (30%;
from 40.38/sentinel to 28.15/sentinel) and Yamaguchi Prefecture (30%; form
54.46/sentinel to 38.35/sentinel). Twenty six Prefectures (55%) were still
in alert level (30.00/sentinel or over). Among the 47 Prefectures, Miyazaki
Prefecture had the highest reported cases per sentinel (55.51), followed
by Fukui Prefecture (53.78), and Yamaguchi Prefecture (39.59). For the
details, refer to the Map of ILI epidemic level at following URL (Japanese only)
In week 50, according to the School absenteeism surveillance report from
Ministry of Health Labor and Welfare (MHLW), 554 schools throughout the
nation have been suspended their all classes due to the influenza A (H1N1)
2009 outbreak in school. In addition, one or several grade was suspended
in 2,434 schools and 6,661 schools have suspended one or several individual
class with multiple infected students.
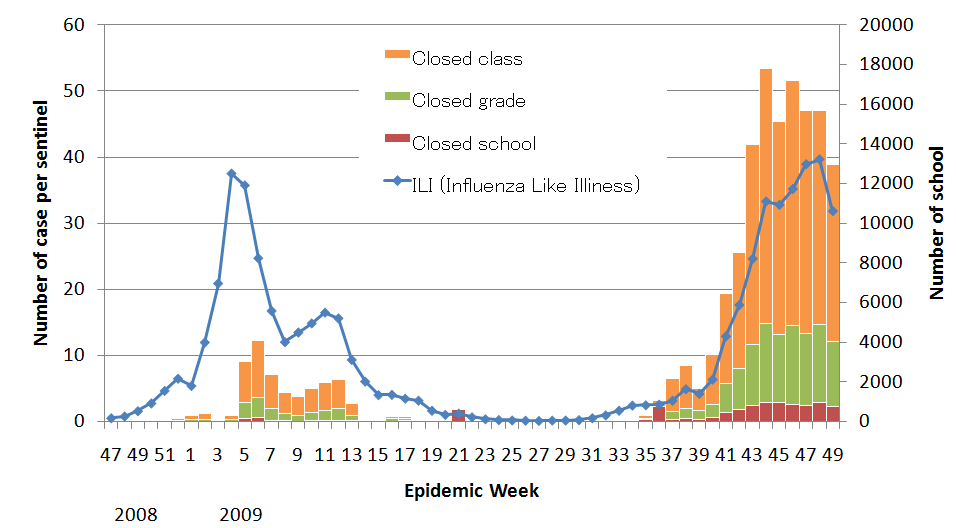
Figure 2. Trend for the number of closed class, grade or school and ILI surveillance
There were 520 reported hospitalization cases due to pandemic influenza AH1pdm infection during December 9 to 15, according to MHLW. By age group, the largest report (220 cases; 42% of all age) remained in the 5-9 year-olds, followed by the 1-4 year-olds (132; 25%) and the 10-14 year-olds (54; 10%). Acute encephalopathy was diagnosed in 13 cases (3%) and mechanical ventilator was used in 18 (3%) among all inpatients.
As of December 15, 2009, cumulative number of the hospitalized cases was 12,923 (Cumulative number of the hospitalized case included case who has already hospitalized on July 28 and new inpatient case on July 29 or later.). Among the hospitalized case, 4,567 cases have some kind(s) of underlying disease, in which 2,961 cases (65%) have had chronic respiratory illness. Cumulative number of the death was 116. Of all fatal cases, 82 cases (71%) have underlying disease.
According to Infectious Agents Surveillance Report, most of the influenza
viruses detected/isolated from specimens of influenza cases during the
week 19 through 50 were AH1pdm (Figure 3).
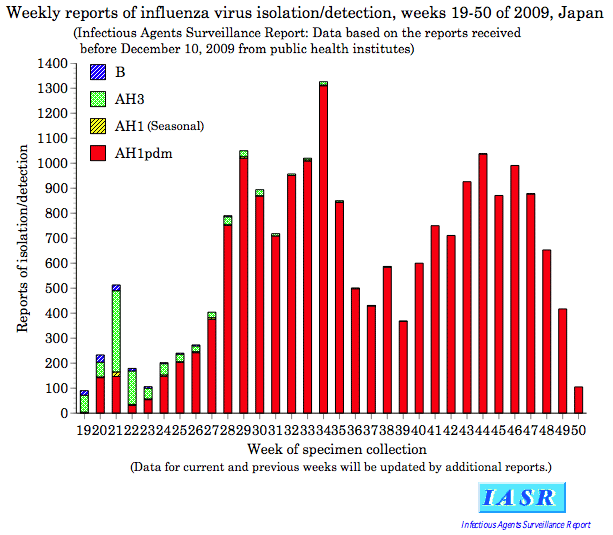
Figure 3. Weekly reports of
influenza virus isolation/detection
* The number of sentinel clinics and hospitals is determined depending
on the relative population of the jurisdiction of each public health center
and on consideration enabling comprehend the incidents in the whole area
of the prefecture. The influenza sentinel points consist of approximately
3,000 pediatric hospitals/clinics and 1,800 internist hospitals/clinics
around the country.
|

